Table of Contents
Get Custom eCommerce Fulfillment Service
Book a Meeting
What Is WMS? A Comprehensive Guide for Warehouse Management Systems
Time: Jul 01,2025 Author: SFC Source: www.sendfromchina.com
Managing a warehouse involves more than just storing products; it requires a system that ensures everything runs smoothly. Enter the Warehouse Management System (WMS)—a software solution designed to oversee and optimize warehouse operations. From tracking inventory to managing shipments, a WMS is essential for businesses aiming to improve efficiency and accuracy. This guide breaks down what a WMS is, its benefits, functionalities, and how it supports e-commerce fulfillment, providing a clear understanding for those new to the concept.
1. What Is WMS?
A Warehouse Management System is a software solution designed to optimize and control warehouse operations. It manages tasks such as inventory tracking, order fulfillment, and shipping, ensuring real-time visibility and efficiency within the warehouse. By automating these processes, a WMS enhances accuracy and productivity, making it an essential tool in modern supply chain management.2. Advantages of Warehouse Management Systems(WMS)
Implementing a Warehouse Management System offers a multitude of benefits that enhance operational efficiency, accuracy, and customer satisfaction. Below are the key advantages: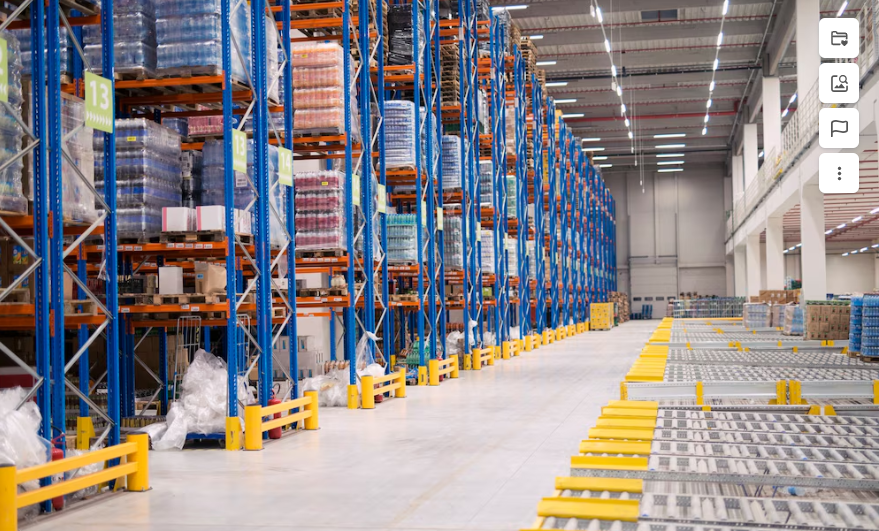
Enhanced Inventory Accuracy
A WMS provides real-time tracking of inventory levels, locations, and movements within the warehouse. By utilizing technologies such as barcode scanning and RFID, businesses can significantly reduce errors associated with manual inventory management. This leads to improved stock accuracy, minimizing instances of overstocking or stockouts, and ensuring that inventory records reflect actual stock levels.Improved Order Fulfillment
With optimized picking and packing processes, a WMS enhances order fulfillment speed and accuracy. By guiding warehouse staff through efficient picking routes and automating packing procedures, the system reduces order processing times and errors. This results in faster delivery times and increased customer satisfaction.Optimized Warehouse Space Utilization
A WMS analyzes warehouse layouts and storage requirements to optimize space utilization. By determining the most efficient storage locations for products based on size, demand, and turnover rates, the system maximizes available space, reduces clutter, and enhances accessibility.Increased Labor Productivity
By automating routine tasks and providing real-time task assignments, a WMS enhances labor productivity. The system allocates tasks based on employee skill sets and proximity, reducing travel time and ensuring efficient use of labor resources. This leads to improved workforce efficiency and reduced labor costs.Real-Time Data and Reporting
A WMS offers real-time data collection and reporting capabilities, providing insights into warehouse operations. Managers can monitor key performance indicators (KPIs), track order statuses, and analyze inventory trends. This data-driven approach facilitates informed decision-making and continuous process improvement.Enhanced Customer Satisfaction
Accurate inventory management and efficient order fulfillment contribute to higher customer satisfaction. By ensuring that customers receive the correct products promptly, a WMS helps build trust and loyalty. Additionally, real-time order tracking enhances transparency and customer confidence in the delivery process.Streamlined Returns Management
Handling returns efficiently is crucial for customer satisfaction and cost control. A WMS streamlines the returns process by tracking returned items, updating inventory records, and facilitating restocking or disposal. This reduces the time and resources required to manage returns and minimizes potential losses.Scalability and Flexibility
As businesses grow, a WMS can scale to accommodate increased inventory volumes and additional warehouse locations. The system's flexibility allows for customization to meet specific operational needs, ensuring that it continues to support business objectives over time.Regulatory Compliance and Traceability
For industries with strict regulatory requirements, a WMS provides the necessary tools for compliance. It maintains detailed records of inventory movements, batch numbers, and expiration dates, facilitating traceability and ensuring adherence to industry standards.Integration with Other Systems
A WMS can integrate seamlessly with other enterprise systems such as Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and Transportation Management Systems (TMS). This integration enables synchronized data flow across various departments, enhancing overall operational efficiency and visibility.3. Functions of Warehouse Management System
A WMS encompasses a comprehensive suite of functionalities designed to optimize warehouse operations. These functions ensure efficient management of inventory, labor, and processes, contributing to overall supply chain effectiveness.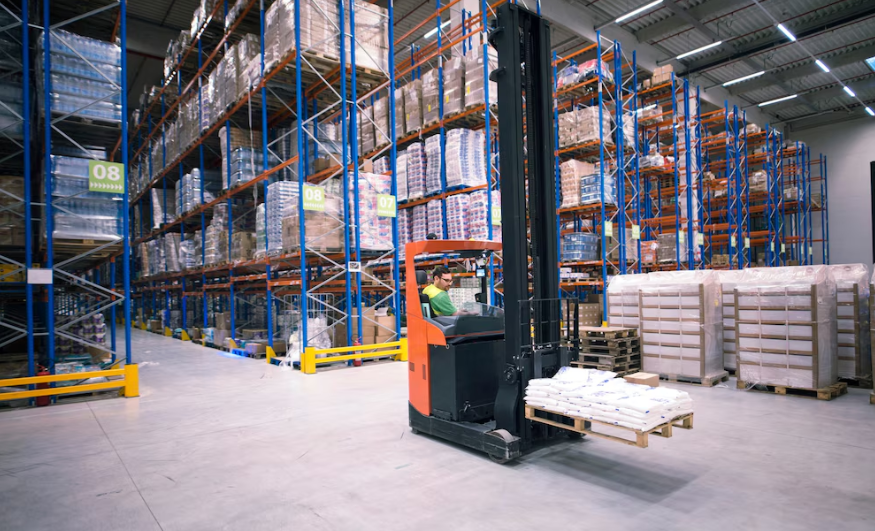
Inventory Management and Control
A WMS provides real-time visibility into inventory levels, locations, and movements within the warehouse. By utilizing technologies like barcode scanning and RFID, it ensures accurate tracking of stock, reducing discrepancies and stockouts. This precise inventory control facilitates better demand forecasting and inventory replenishment strategies.Receiving and Putaway
Upon the arrival of goods, the WMS streamlines the receiving process by verifying shipments against purchase orders, identifying discrepancies, and updating inventory records. It then directs the putaway process, assigning optimal storage locations based on factors like product type, size, and turnover rate, thereby maximizing space utilization and accessibility.Order Picking and Packing
The WMS enhances order fulfillment by generating efficient picking lists and routes, minimizing travel time within the warehouse. It supports various picking methods, such as batch picking and zone picking, tailored to the warehouse's operational needs. During packing, the system ensures correct item selection and packaging, reducing errors and returns.Shipping and Dispatch
In the shipping phase, the WMS coordinates the consolidation of orders, label generation, and carrier selection. It ensures that shipments are accurately documented and dispatched on time, improving delivery performance and customer satisfaction.Labor Management
A WMS monitors workforce activities, assigning tasks based on employee availability and skill sets. It tracks performance metrics, enabling managers to identify productivity trends and areas for improvement. This function aids in optimizing labor allocation and reducing operational costs.Reporting and Analytics
The system generates comprehensive reports on various aspects of warehouse operations, including inventory levels, order fulfillment rates, and labor productivity. These analytics provide actionable insights for strategic decision-making and continuous improvement initiatives.Returns Management
Handling returns efficiently is crucial for customer satisfaction. A WMS manages the reverse logistics process by tracking returned items, updating inventory records, and facilitating restocking or disposal decisions. This function ensures transparency and accountability in returns processing.Integration with Other Systems
Modern WMS solutions are designed to integrate seamlessly with other enterprise systems, such as Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and Transportation Management Systems. This integration enables synchronized data flow across the organization, enhancing overall supply chain coordination.4. Types of Warehouse Management Systems
It's essential to understand the various WMS types to select the one that best aligns with your business needs. Each type offers distinct features, advantages, and considerations.
Standalone Warehouse Management Systems
Standalone WMS solutions are specialized software applications focused solely on warehouse operations. They are ideal for businesses seeking robust warehouse functionalities without the need for broader enterprise integration.Key Features:
- Inventory tracking
- Order picking and packing
- Shipping management
- Barcode scanning
Advantages:
- Tailored functionalities for warehouse operations
- Often more affordable than integrated systems
- Simplified implementation
Considerations:
- Limited integration with other business systems
- May require manual data transfer between systems
Ideal for small to medium-sized businesses focusing primarily on warehouse efficiency.
Supply Chain Module WMS
This type of WMS is integrated within a broader Supply Chain Management (SCM) system, offering a holistic view of the supply chain, including procurement, manufacturing, and distribution.Key Features:
- End-to-end supply chain visibility
- Integration with transportation and procurement systems
- Advanced analytics for demand forecasting
Advantages:
- Enhanced coordination across the supply chain
- Improved demand planning and inventory optimization
- Streamlined communication with suppliers and distributors
Considerations:
- Higher complexity and cost
- Requires comprehensive training for effective use
Suitable for large enterprises with complex supply chain operations.
ERP-Integrated WMS
An ERP-integrated WMS is a module within an Enterprise Resource Planning system, providing seamless integration between warehouse operations and other business functions like finance, HR, and sales.Key Features:
- Unified data across departments
- Real-time inventory and financial reporting
- Streamlined order processing
Advantages:
- Eliminates data silos
- Improves cross-departmental collaboration
- Facilitates strategic decision-making
Considerations:
- May lack specialized warehouse functionalities
- Implementation can be resource-intensive
Best suited for organizations already utilizing an ERP system seeking integrated warehouse management.
Cloud-Based WMS
Cloud-based WMS solutions are hosted on remote servers, accessible via the internet, offering scalability and flexibility without the need for extensive on-premise infrastructure.Key Features:
- Remote access from any location
- Automatic software updates
- Scalable resources based on demand
Advantages:
- Lower upfront costs
- Quick deployment
- Reduced IT maintenance
Considerations:
- Dependence on internet connectivity
- Potential concerns over data security
Ideal for businesses seeking cost-effective, scalable, and easily deployable warehouse management solutions.
5. How Warehouse Management Systems Work?
A Warehouse Management System functions as the central nervous system of warehouse operations, coordinating and optimizing various processes to ensure efficiency, accuracy, and real-time visibility. Here's an in-depth look at how WMS operates:
Data Collection and Integration
A WMS begins by collecting data from various sources within the warehouse, such as barcode scanners, RFID tags, and manual entries. This data encompasses information about inventory levels, locations, order statuses, and more. The system integrates this data to provide a comprehensive view of warehouse operations, enabling informed decision-making and streamlined processes.Inventory Management
Real-time inventory tracking is a cornerstone of WMS functionality. By continuously monitoring stock levels and locations, the system ensures accurate inventory records, reduces discrepancies, and minimizes stockouts or overstock situations. This real-time visibility allows for efficient inventory control and supports demand forecasting.Receiving and Putaway
Upon receiving goods, the WMS verifies shipments against purchase orders, identifies discrepancies, and updates inventory records. It then directs the putaway process by suggesting optimal storage locations based on factors like product type, size, and turnover rate. This strategic placement maximizes space utilization and facilitates easy retrieval.Order Processing and Picking
When an order is placed, the WMS generates a picking list and determines the most efficient picking strategy, such as zone, batch, or wave picking. It guides warehouse staff through the picking process using handheld devices or voice-directed systems, ensuring accurate and timely order fulfillment.Packing and Shipping
After picking, the WMS oversees the packing process, ensuring that items are correctly packaged and labeled. It then coordinates shipping by selecting appropriate carriers, generating shipping documents, and updating order statuses. This streamlined process enhances delivery accuracy and customer satisfaction.Labor Management
A WMS monitors workforce activities, assigning tasks based on employee availability and skill sets. It tracks performance metrics, enabling managers to identify productivity trends and areas for improvement. This function aids in optimizing labor allocation and reducing operational costs.Reporting and Analytics
The system generates comprehensive reports on various aspects of warehouse operations, including inventory levels, order fulfillment rates, and labor productivity. These analytics provide actionable insights for strategic decision-making and continuous improvement initiatives.6. Tips to Choose a Warehouse Management System
Selecting the right Warehouse Management System is a pivotal decision that can significantly impact your warehouse operations, efficiency, and scalability. With a multitude of options available, it's essential to approach this selection methodically. Here are key considerations to guide you in choosing the most suitable WMS for your business:
Assess Your Operational Needs
Begin by conducting a thorough analysis of your current warehouse operations. Identify pain points, inefficiencies, and areas where automation could bring improvements. Consider factors such as inventory volume, order complexity, and the need for real-time tracking. Understanding your specific requirements will help in selecting a WMS that aligns with your operational goals.Define Clear Objectives
Establish what you aim to achieve with the new WMS. Whether it's reducing order processing time, improving inventory accuracy, or enhancing customer satisfaction, having clear objectives will guide your selection process and help in evaluating the effectiveness of the system post-implementation.Ensure Scalability and Flexibility
Choose a WMS that can scale with your business growth and adapt to changing operational needs. The system should be flexible enough to accommodate new processes, integrate with additional modules, and support expansion into new markets or product lines.Evaluate Integration Capabilities
A WMS should seamlessly integrate with your existing systems such as ERP, CRM, and transportation management systems. This integration ensures smooth data flow across departments, reduces manual data entry, and minimizes errors.Consider User-Friendliness
The system should have an intuitive interface that is easy for your team to learn and use. A user-friendly WMS reduces training time, minimizes errors, and enhances overall productivity. Ensure that the vendor provides adequate training and support during and after implementation.Analyze Total Cost of Ownership
Beyond the initial purchase price, consider the total cost of ownership, including implementation, training, maintenance, and potential upgrades. Assess the return on investment by evaluating how the WMS will contribute to cost savings and efficiency improvements over time.Check Vendor Reputation and Support
Research the vendor's track record, customer reviews, and industry reputation. A reliable vendor should offer robust customer support, regular system updates, and a clear roadmap for future enhancements. Engage with existing clients to gather insights into their experiences with the vendor.Request Demonstrations and Trials
Before finalizing your decision, request demonstrations or trial periods to evaluate the WMS in a real-world setting. This hands-on experience will help you assess the system's performance, compatibility with your operations, and ease of use.Plan for Implementation and Change Management
Develop a comprehensive implementation plan that includes timelines, resource allocation, and change management strategies. Involve key stakeholders from various departments to ensure a smooth transition and buy-in across the organization.Monitor and Evaluate Performance
Post-implementation, continuously monitor the WMS's performance against your predefined objectives. Gather feedback from users, track key performance indicators, and be prepared to make adjustments to optimize the system's effectiveness.7. The Role of WMS in E-commerce Fulfillment
In the dynamic world of e-commerce, where customer expectations for rapid and accurate deliveries are ever-increasing, Warehouse Management Systems have become indispensable. A robust WMS not only streamlines warehouse operations but also enhances the overall fulfillment process, ensuring customer satisfaction and business growth. Here's an in-depth look at how WMS plays a pivotal role in e-commerce fulfillment:
Real-Time Inventory Management
E-commerce businesses often operate across multiple sales channels, making real-time inventory visibility crucial. A WMS provides up-to-the-minute tracking of stock levels, locations, and movements within the warehouse. This real-time data helps prevent stockouts and overstock situations, ensuring that popular items are always available for customers. Moreover, accurate inventory records facilitate better demand forecasting and inventory replenishment strategies.Optimized Order Fulfillment
Speed and accuracy in order processing are vital in e-commerce. A WMS automates the picking, packing, and shipping processes, reducing manual errors and increasing efficiency. By utilizing intelligent algorithms, the system determines the most efficient picking routes and packing methods, ensuring that orders are fulfilled promptly and accurately. This optimization leads to faster delivery times and higher customer satisfaction.Seamless Integration with E-commerce Platforms
Modern WMS solutions are designed to integrate seamlessly with various e-commerce platforms such as Shopify, Amazon, and Magento. This integration ensures that order information flows smoothly between the online store and the warehouse, enabling real-time updates on inventory levels and order statuses. Such synchronization minimizes the risk of overselling and enhances the overall customer experience.Enhanced Returns Management
Returns are an inevitable part of e-commerce. A WMS streamlines the returns process by tracking returned items, updating inventory records, and facilitating restocking or disposal decisions. Efficient returns management not only improves customer satisfaction but also helps in reclaiming the value of returned products promptly.Scalability and Flexibility
E-commerce businesses often experience fluctuations in order volumes due to seasonal trends or promotional campaigns. A scalable WMS can adapt to these changes, allowing businesses to handle increased workloads without compromising efficiency. Whether it's adding new sales channels or expanding to new markets, a flexible WMS supports business growth seamlessly.Improved Customer Satisfaction
By ensuring accurate inventory levels, timely order fulfillment, and efficient returns processing, a WMS directly contributes to enhanced customer satisfaction. Customers receive their orders promptly and can trust the reliability of the service, leading to increased loyalty and repeat business.8. Conclusion
A Warehouse Management System is integral to modern warehouse operations, offering enhanced efficiency, accuracy, and adaptability. By understanding its functions, types, and benefits, businesses can make informed decisions to optimize their warehouse management and meet the evolving demands of the market.9. FAQs
Q1: What is the primary purpose of a WMS?
A WMS aims to streamline warehouse operations, improving efficiency and accuracy in inventory management and order fulfillment.Q2: Can a WMS integrate with other business systems?
Yes, many WMS solutions can integrate with ERP, CRM, and other systems for seamless data flow.Q3: Is a cloud-based WMS better than an on-premise one?
It depends on your business needs. Cloud-based WMS offers scalability and remote access, while on-premise systems provide more control.Q4: How does a WMS improve customer satisfaction?
By ensuring accurate and timely order fulfillment, a WMS enhances the overall customer experience.Q5: What factors should I consider when choosing a WMS?
Consider scalability, integration capabilities, user-friendliness, vendor support, and cost. Post Views:1440
Post Views:1440
Copyright statement: The copyright of this article belongs to the original author. Please indicate the source for reprinting.
Previous Post
What Is First Mile Delivery? A Complete Guide for Ecommerce Logistics
Next Post
TAGS
Hot Research
Get Custom eCommerce Fulfillment Service
Book a Meeting
Get a Custom China Fulfillment Solution with FREE Storage for 30 Days
 Want to know about our services, fees or receive a custom quote?
Want to know about our services, fees or receive a custom quote?
 Please fill out the form on the right and we will get back to you within a business day.
Please fill out the form on the right and we will get back to you within a business day.
 The more information you provide, the better our initial response
will be.
The more information you provide, the better our initial response
will be.




 TAGS:
TAGS: