Table of Contents
Supply Chain Quality Matters: Top KPIs, Challenges & Optimization Strategies
Time: Jul 22,2025 Author: SFC Source: www.sendfromchina.com
In today’s complex global marketplace, supply chain quality isn’t just about moving goods efficiently—it’s about ensuring every component meets exacting standards from end to end. When supply chains falter, brands risk costly recalls, unhappy customers, and shattered reputations. But when quality is baked into every link—from raw materials to final delivery—businesses reap rewards in operational efficiency, customer loyalty, and sustained growth.This comprehensive guide will walk you through:
- What supply chain quality really means
- Why it’s critical for cost control, risk mitigation, and brand trust
- The key metrics that reveal hidden weak spots
- Tangible benefits of optimization
- Major challenges that often trip up companies
Whether you're managing logistics, procurement, or fulfillment for a growing e-commerce brand, this post combines real-world insights, data-backed frameworks, and proven best practices. Let’s dive in—and discover how elevating supply chain quality can transform your bottom line and competitive edge.

1. What Is Supply Chain Quality
Supply chain quality is more than a buzzword—it’s the backbone of reliable logistics and product delivery. It refers to the ability of every step—from sourcing raw materials to delivering finished goods—to meet and maintain defined standards. It includes product integrity, service excellence, compliance, and consistency across global operations.Let's break it down further:
- Product standard compliance: Does each component arrive intact, untainted, and up to spec?
- Process integrity: Are workflows—like manufacturing, packaging, and shipping—executed flawlessly every time?
- Inter‑partner coordination: Are suppliers, manufacturers, logistics providers all on the same page?
- Regulatory adherence: Are safety, environmental, and industry regulations met consistently?
In essence, supply chain quality is about maintaining excellence at every node—so goods travel through the system unharmed, accurately, and on schedule.
2. Why Supply Chain Quality Matters
Investing in supply chain quality isn’t a luxury—it’s foundational. When every link upholds its standard, the results ripple outward: satisfied customers, controlled costs, and a resilient, market-leading business.
Enhanced Customer Satisfaction & Loyalty
When quality is prioritized, customers consistently receive the right products—intact, on time, and matching expectations. This builds genuine loyalty.- A study found that service quality, delivery speed, and pricing transparency directly boost customer satisfaction and trust—especially in global marketplaces.
- Aptean notes the supply chain often forms "the hidden weapon" for delighting customers, shaping their service, pricing, and repeat purchase behaviors.
Slashed Costs & Operational Efficiency
Quality cuts waste. Errors, returns, and rework all drain margins. Maintaining high standards means fewer scrapped shipments and lower internal failure costs.- Chron points out that weak quality controls lead to excess waste and damage downstream efficiency.
- IBM echoes this: building quality in helps avoid legal issues and rescue reputations on the brink of collapse.
Brand Reputation & Competitive Edge
In today’s social media era, one bad delivery or defective item can trigger viral backlash. Reliability becomes a competitive differentiator.- Deloitte reveals that many executives overestimate customer trust—only quality delivers the public loyalty they assume exists.
- Qualityze emphasizes that compliance and excellence are non-negotiable in regulated industries to maintain consumer and audit confidence.
Risk Mitigation & Regulatory Compliance
Product recalls, legal penalties, and market withdrawals originate from quality lapses. Embedding quality reduces these risks.- Strict quality systems streamline adherence to safety and environmental regulations, shielding companies from fines and public scrutiny.
- Proactive risk strategies enhance resilience, minimizing the aftermath of supply disruptions.
Supply Chain Resilience & Agility
Quality is tightly linked with resilience. Streamlined processes and robust controls empower systems to adapt quickly under pressure.- Studies show that flexible, quality-driven supply chains are better prepared to withstand disruptions, whether pandemic, cyberattack, or logistics breakdown.
- The Financial Times highlights the role of real-time tracking—GPS, RFID, AI—in pre-empting weak links and reinforcing overall resilience.
Continuous Improvement Culture
Shipping flawless products fosters a culture of ongoing refinement. Mistakes become lessons, not repeat failures.- The SCS Framework calls quality the “lifeblood” of continuous improvement—regular performance reviews kindle betterment.
- Achilles adds that a standardized Quality Management System across suppliers helps detect weak points and elevate entire networks.
3. Key Metrics & KPIs for Supply Chain Quality
“To improve what you don’t measure is impossible.” Effective supply chain quality optimization starts with tracking the right metrics—precision tools that spotlight inefficiencies and opportunities for improvement.
Perfect Order Rate (POR)
The percentage of orders delivered flawlessly—correct items, quantity, condition, documentation, and timing.Formula:
Perfect Order Rate = (Perfect Orders ÷ Total Orders) × 100%
- A “perfect” order meets all these conditions: on-time, in-full, undamaged, accurately invoiced, correct documentation—and more.
- Because it consolidates multiple dimensions, POR offers a holistic lens on customer satisfaction and internal alignment.
Why it matters
- Measures the end-to-end supply chain health in one KPI.
- High POR correlates strongly with loyalty, reduced costs, and operational coherence.
OTIF / DIFOT (On-Time In-Full / Delivery In Full On Time)
The ratio of orders that arrive both complete and on schedule, viewed from the customer's expected delivery window.Formula:
OTIF = (Orders Delivered On Time AND In Full ÷ Total Orders) × 100%
- Complements POR by emphasizing only “time + quantity.”
- Industry benchmark (e.g., UK retail) often targets >97% at SKU level.
Delivery Schedule Adherence (DSA)
Tracks supplier reliability—how consistently they meet agreed delivery dates and quantities.Formula:
DSA = (On-Time Deliveries ÷ Total Deliveries) × 100%
- A low DSA results in buffer stock, increased costs, and shortage risk.
- Supports supplier performance evaluation and ranking.
Inventory Turnover
Reflects inventory efficiency—the speed at which stock moves from receipt to sale.Formula:
Inventory Turnover = Cost of Goods Sold ÷ Average Inventory
- Higher turnover = leaner operation, reduced holding costs.
- Balances order readiness with cost-effective inventory management.
Lead Time Metrics
Types:- Customer Order Cycle Time: Time from order placement to customer delivery.
- Supply Chain Cycle Time: Time needed to fulfill an order if starting from zero inventory.
Why they matter:
- Shorter lead times = quicker response to customer demand.
- Long lead times can hide quality issues and inflate carrying costs.
Cash-to-Cash Cycle Time
How long cash is tied up—between supplier payment and customer payment.Formula:
Cash-to-Cash Cycle = Days Inventory Outstanding + Days Sales Outstanding – Days Payable Outstanding
- Quality disruptions (returns, rework) slow this cycle—impacting cash and profitability.
Fill Rate & Perfect Case Fill Rate
Fill Rate: Percentage of customer demand fulfilled immediately from stock.Perfect Case Fill Rate: Orders shipped correctly on first pick, in full.
- High fill rates = fewer backorders, higher customer trust.
- Poor rate leads to re-picks, increased labor, and unsatisfied customers.
Supplier Quality Performance (SQP) & Return/Defect Rates
SQP: Tracks supplier consistency and defect-free deliveries.Return/Defect Rate: Percentage of products returned or found defective.
- Both align with POR and OTIF—spotting trouble early.
- High performance here improves margins and brand reputation.
Freight Bill Accuracy & Cost Metrics
Freight Bill Accuracy: Percentage alignment between service and invoice.Freight Cost per Unit: Average transport cost per unit shipped.
- Ensures transparency and flags billing irregularities in logistics.
Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT)
Definition: Post-delivery customer surveys score satisfaction related to service, delivery, and quality.- Though subjective, CSAT often reveals early warning signs when performance metrics dip.
4. Benefits of Optimizing Supply Chain Quality
Optimizing supply chain quality isn't just a goal—it’s a strategic imperative that drives measurable gains across costs, efficiency, resilience, and brand equity.
Cost Reduction & Higher Margins
Fewer defects, less rework, minimized returns, and smoother logistics shrink expenses across the board.Faster Delivery & Higher Throughput
With less disruption, fulfillment times drop. AI integration in last‑mile logistics, for instance, boosts speed and accuracy.Better Inventory Management
Quality‑focused metrics lead to more precise inventory management—not too much, not too little. This reduces both shortage and excess risk.Stronger Supplier Relationships
Focusing on metrics encourages collaborative quality improvement with suppliers. It shifts culture from “blame” to shared responsibility. Brands like Gobi Cashmere credit vertical integration and trust-based partnerships for consistency.Brand Differentiation & Customer Loyalty
Consistency breeds trust. When your deliveries are invariably flawless, customers remember—and repeat.Greater Resilience
Monitoring traceability, quality and fulfillment KPIs tighter translates to early warning systems for disruptions like weather events, geopolitical issues, and supplier failures.Sustainability Gains
Efficient supply chain quality means reduced waste, better route planning, lower carbon emissions—win for business + planet.5. Key Challenges When Maintaining Supply Chain Quality
Ensuring high-quality standards across a complex supply chain isn’t easy. Global networks, multiple suppliers, and ever-changing variables mean that even minor missteps can cascade into major issues. Here are the most common and pressing challenges:
Complexity of Global & Fragmented Networks
Challenge: Managing suppliers across geographies—each with its own regulations, standards, and logistics workflows—can lead to fragmented processes and inconsistent quality.- Modern supply chains involve multi-tiered suppliers, 3PLs, customs checkpoints, and differing safety norms, increasing error risk. One study noted that diverse fulfillment partners cause variations in quality and compliance across regions.
- The “bullwhip effect”—where small fluctuations in demand are amplified upstream—exacerbates instability, causing inefficiencies and stock inconsistencie.
Visibility Gaps & Data Silos
Challenge: Lack of end-to-end real-time insights leads to blind spots, making it tougher to anticipate issues or enforce standards consistently.- NetSuite reports that insufficient visibility is one of the top reasons disruptions go undetected until they escalate.
- Over-reliance on outdated systems—like fragmented email chains, spreadsheets, or fax—furthers data disconnects, hindering efficiency.
Supplier Reliability & Quality Assurance
Challenge: Suppliers may follow varying procedures or standards, and without consistent quality checks, defect and reliability rates fluctuate.- Ensuring consistent quality across multiple supplier tiers remains one of the most significant obstacles.
- Cultural and communication differences between partners can lead to misinterpretations, delays, and misaligned standards.
Material Shortages & Intentional Imbalances
Challenge: Interruptions in raw material supply—due to scarcity, geopolitics, or natural disasters—create buffering, substitution risks, and potential quality downgrades.- Over 60% of global companies report raw material shortages as a major disruption risk.
- In trying to meet demand, companies may switch to secondary suppliers or alternate materials, increasing the risk of quality inconsistencies—even causing batch-level variations.
Rising Transportation Costs & Port Congestion
Challenge: Increased freight prices and delays at port entry exert pressure on lead times and may incentivize cost reductions at the expense of quality.- Rising shipping, traffic, and fuel costs, combined with port bottlenecks, force operational slowdowns and thinner margins.
- To adjust, companies may rush shipments, skip inspection steps, or switch carriers mid-stream—each raising quality failure risk.
Technological Integration & Digital Transformation
Challenge: Adoption of modern tech—ERP, AI, IoT, blockchain—is uneven, creating integration issues and inconsistent data capture.- Many supply chains lag in integrating automation, AI analytics, predictive tools, and blockchain traceability.
- Connectivity issues—disparate systems, lack of real-time data sharing—hinder seamless process control.
Communication Gaps & Coordination Breakdown
Challenge: Misaligned objectives, inconsistent updates, and disconnected teams lead to errors, delays, and fractured execution.- Without centralized communication systems, fragmented channels result in misinterpretation and inefficiencies.
- Supplier relationship issues—arising from communication missteps—are a leading cause of unreliable delivery and quality variance.
Regulatory Complexity & Compliance
Challenge: Global regulations are constantly evolving—covering materials, labeling, safety, emissions. Staying updated is resource-intensive.- Companies must maintain audit-ready documentation and stay on top of shifting regulations—from environmental mandates to labor standards. Lapses risk fines or forced recalls.
- Food, pharma, electronics, and apparel supply chains (e.g., sourcing cotton from Xinjiang) increasingly require traceability and compliance with human-rights standards.
Disruption Risk: Cybersecurity, Pandemics, Weather
Challenge: External shocks—cyberattacks, pandemics, climate events—can undermine system integrity, halt operations, and distort quality processes.- The UNFI/Whole Foods cyber incident highlighted how an attack can freeze distribution, leading to empty shelves and compromised fulfilment.
- Similarly, port closures, labor strikes, or climate-induced disasters introduce delays and unpredictable supplier behavior.
Cost vs. Quality Trade-Offs
Challenge: Tight budgets often pressure teams to cut corners—skimp on inspections, reduce holding buffers, or skip supplier audits.- Cost containment measures—like reserving minimal stock or enforcing tight delivery windows—can compromise product standards.
- Companies struggle to balance lean inventory with the buffers required for quality assurance.
6. How to Optimize Supply Chain Quality
Elevating supply chain quality requires a multi-layered approach—from setting clear benchmarks to integrating cutting-edge technologies and fostering collaboration.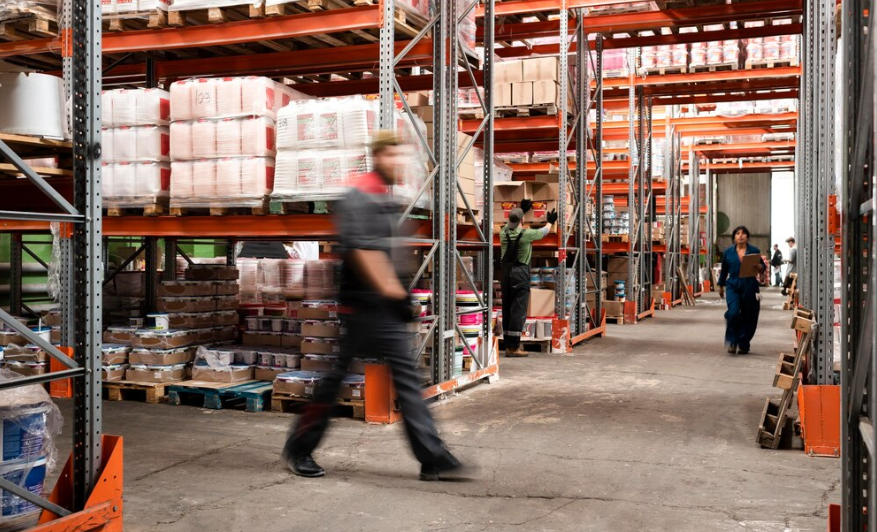
Define & Align Quality Metrics
Start by choosing KPIs that align with your strategic objectives—such as Perfect Order Rate, OTIF, supplier defect rates, and cash-to-cash cycle time. Then:- Benchmark against industry standards to set targets. For example, best-in-class OTIF sits around 97%+.
- Roll out metrics across tiers—from tier-1 suppliers to 3PLs—to ensure accountability at every level.
- Review dashboards regularly to identify underperforming nodes and take corrective action.
Structured metrics build clarity, focus, and continuous improvement momentum.
Invest in Technology & Automation
Modern tools can enforce quality measures and reduce human errors:- Warehouse & Transport Systems: WMS and TMS automate quality checks—like barcode scans, condition alerts, and pick accuracy verifications.
- AI & Machine Learning: AI-driven routing (e.g., Amazon Wellspring, UPS DeliveryDefense) enhances delivery reliability and detects delivery failures in real-time.
- IoT & RFID: Sensors capture temperature, humidity, and location data—making quality condition breaches visible.
- Blockchain & Visibility Platforms: Immutable ledgers support transparency from source to shelf, crucial for audits and traceability.
Implement Supplier Collaboration & Audits
Strong supplier relationships are built on shared accountability:- Broaden audit scope: Don’t limit quality reviews to just top-tier vendors—sparta systems found that most only assess less than ⅓ of their supply base, increasing risk.
- Scorecards & feedback loops: Share performance data (e.g., defect rates, delivery reliability) to drive continuous supplier improvement.
- Incentives & penalties: Use contract terms or collaborative quality programs to reward high-performing partners and discourage underperformance.
Standardize Processes & Leverage Lean Approaches
Consistency is key to reducing variation and errors:- Value-Stream Mapping: Visually document and optimize flow—identifying and eliminating non-value steps.
- Lean Six Sigma & Kaizen: Apply waste reduction, root-cause analysis, and incremental improvement methods. These have driven billions in savings for companies like GE and Motorola.
- Total Quality Management (TQM): Foster a culture where every stakeholder owns quality—from design to dispatch—mirroring Toyota’s Kanban excellence.
Build Real-Time Visibility & Control Towers
When you can see, you can solve:- Digital control towers visualize key indicators—like delays, temperature breaches, supplier defects—in real time.
- CPFR (Collaborative Planning, Forecasting & Replenishment): Share forecasts and inventory needs with partners to reduce order variability and stockouts.
- Scenario modeling with digital twins: Simulate disruptions and responses to optimize resilience before issues arise.
Foster Continuous Improvement & Change Management
Quality is not a one-time project—it’s culture:- Establish a cross-functional supply chain council to govern standards, KPIs, processes, and corrective actions.
- Encourage Kaizen: Empower frontline staff to flag issues and suggest process tweaks. Small changes can have large ripple effects.
- Change management: Communicate, train, and align teams around quality goals. APQC finds structured change plans are key to sustaining improvement.
Enhance Traceability & Transparency
Traceability builds trust and enables fast responses:- Track provenance: Record source, batch, and transit info for materials to support recall readiness and verification audits.
- Vertical integration & local sourcing: As Gobi Cashmere and AGI Denim show, direct control over material flow boosts quality consistency—but requires balanced regional sourcing strategies.
- Audit trails & sharing: Capture inspection data that both internal teams and partners can access to align on quality outcomes.
Optimize Last‑Mile Quality
Delivery is the final—and visible—quality checkpoint:- Route Optimization with AI: Real-time route adjustments minimize delays, theft, and damage during delivery.
- Predictive Maintenance & Damage Alerts: AI platforms track delivery patterns to flag at-risk orders ahead of issues.
- Customer visibility & recovery orchestration: Proactive updates and rapid interventions prevent poor delivery experiences.
Monitor & Tune Performance
Ensure your efforts stick:- Regular KPI reviews: Analyze dashboards weekly and monthly for POR, OTIF, defect rates, and CSAT to spot trends and performance dips.
- Root‑cause investigation: When KPI deviations occur, conduct structured investigations (5 Whys, etc.) to implement durable fixes.
- Iterate relentlessly: Continuous testing—small pilots, process refinements, tool integrations—drives lasting improvements.
7. Conclusion
Optimizing supply chain quality isn’t optional—it’s essential. It guards profit margins, brand trust, operational resilience, and long‑term competitiveness. When you track the right KPIs, invest in the right tools, partner with your supply network, and sustain a culture of continuous improvement, quality isn’t just a goal—it becomes a competitive moat.In today’s fast, transparent, traceable marketplace, quality is the quiet engine of success.
8. FAQs
1. What is the most important KPI for supply chain quality?
The Perfect Order Rate—capturing on‑time, full, correct, undamaged delivery—is often seen as the primary benchmark for end‑to‑end quality.2. How does AI improve supply chain quality?
AI enables predictive analytics for route optimization, theft prevention, and condition monitoring—helping identify and address issues before they affect delivery.3. Why is visibility so critical to quality?
Visibility gives real-time insights across suppliers, transport, warehousing—without it, blind‑spots lead to errors, delays, and weak compliance.4. What’s the ROI of quality improvements?
High-quality processes reduce rework, returns, waste, and errors—often saving millions, while boosting customer loyalty and minimizing legal or reputational risks.5. How to handle quality when working with multiple countries?
Standardize protocols, run frequent audits, use technology (RFID, IoT, blockchain) to maintain consistency, and foster trust via communication and partnerships. Post Views:1594
Post Views:1594
Copyright statement: The copyright of this article belongs to the original author. Please indicate the source for reprinting.
Previous Post
Inventory Backlog Explained: Definition, Formulas, and Prevention Strategies
Next Post
Sites Like AliExpress: Best Alternatives for Clothing, Electronics & More (2025)
TAGS
Hot Research
Get a Custom China Fulfillment Solution with FREE Storage for 30 Days
 Want to know about our services, fees or receive a custom quote?
Want to know about our services, fees or receive a custom quote?
 Please fill out the form on the right and we will get back to you within a business day.
Please fill out the form on the right and we will get back to you within a business day.
 The more information you provide, the better our initial response
will be.
The more information you provide, the better our initial response
will be.




 TAGS:
TAGS: