Table of Contents
Fulfillment Center vs. Warehouse 2025: What Are the Differences
Time: Jun 05,2025 Author: SFC Source: www.sendfromchina.com
In the rapidly evolving world of logistics and supply chain management, understanding the distinctions between fulfillment centers and warehouses is crucial for businesses aiming to optimize their operations. As we move further into 2025, these facilities continue to adapt, driven by technological advancements and changing consumer expectations.The choice between utilizing a fulfillment center or a warehouse depends on various factors, including the nature of the products, the speed of delivery required, and the overall business model. As the logistics landscape continues to evolve, businesses must assess their specific needs to determine the most effective solution for their supply chain strategy.
In this article, we will delve deeper into the functions and operations of fulfillment centers and warehouses, compare their differences, and explore how emerging trends in 2025 are reshaping these critical components of the supply chain.

1. What Is a Fulfillment Center?
A fulfillment center is a specialized facility designed to manage the entire order fulfillment process for businesses, particularly in the e-commerce sector. Unlike traditional warehouses that primarily focus on storing goods, fulfillment centers handle a range of operations, including receiving inventory, storing products, picking and packing orders, and shipping them directly to customers . These centers play a pivotal role in ensuring that online orders are processed efficiently and delivered promptly, meeting the high expectations of today's consumers.Types of Fulfillment Centers
Fulfillment centers vary based on their operational focus and the specific needs of the businesses they serve:- E-commerce Fulfillment Centers: Tailored for online retailers, these centers prioritize rapid order processing and direct-to-consumer shipping. They are equipped with advanced technologies to handle high volumes of small parcel shipments efficiently.
- Retail Fulfillment Centers: These facilities distribute products to physical retail locations, supporting businesses with both online and brick-and-mortar presences. They manage bulk shipments and ensure timely replenishment of store inventories.
- Third-Party Logistics (3PL) Fulfillment Centers: Operated by external providers, 3PL centers manage logistics for multiple clients, offering scalability and expertise. They provide a range of services, from inventory management to shipping, allowing businesses to outsource their fulfillment operations.
- Specialized Fulfillment Centers: These centers cater to specific industries or product types, such as perishable goods, hazardous materials, or oversized items. They are equipped with specialized storage and handling capabilities to meet unique requirements.
- Micro-Fulfillment Centers: Located in urban areas, these compact centers are designed for rapid order fulfillment, reducing delivery times and costs by being closer to the end customer. They are increasingly used for same-day or next-day delivery services.
How Fulfillment Centers Work
The operation of a fulfillment center involves several key steps, each critical to ensuring efficient order processing and customer satisfaction:- Receiving Inventory: Products from manufacturers or suppliers are delivered to the center. Upon arrival, items are inspected for quality, counted, and logged into the inventory management system. This step ensures accurate stock levels and readiness for order fulfillment.
- Storage: Items are stored in organized locations within the facility, often using advanced shelving systems and automation to maximize space and accessibility. The storage strategy may vary based on product type and demand.
- Order Processing: When a customer places an order, the system retrieves the relevant information, and staff or automated systems pick the items from storage. Advanced technologies, such as barcode scanning and warehouse management systems, are employed to ensure accuracy and efficiency.
- Packing: Selected items are packed securely, often with branded materials, to ensure safe transit. Packaging may also include promotional materials or customized inserts to enhance the customer experience.
- Shipping: Orders are dispatched using various carriers, with tracking information provided to customers. Fulfillment centers often have partnerships with multiple shipping providers to offer a range of delivery options and optimize shipping costs.
- Returns Management: Fulfillment centers also handle returns, inspecting and restocking items as necessary. Efficient returns processing is essential for maintaining customer satisfaction and managing inventory levels.
2. What Is a Warehouse?
A warehouse is a dedicated facility used for the storage of goods and materials. Unlike fulfillment centers, which focus on processing and shipping orders directly to customers, warehouses primarily serve as storage hubs within the supply chain. They play a critical role in managing inventory, ensuring that products are stored safely and are readily available when needed for distribution or sale.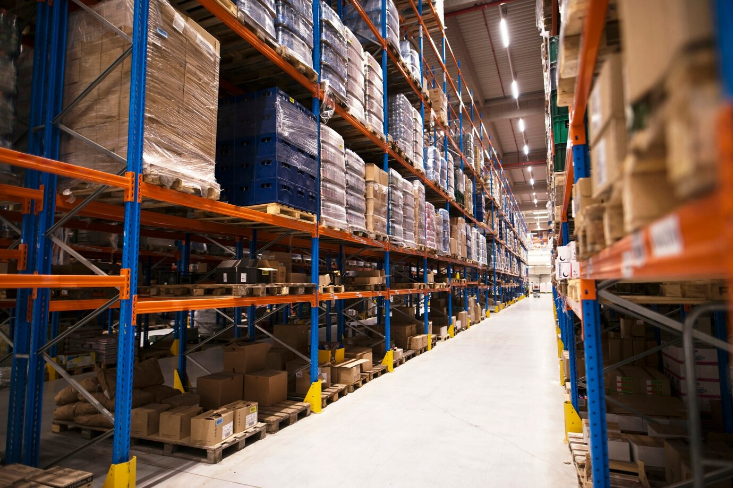
Types of Warehouses
Warehouses come in various forms, each designed to meet specific storage needs:- Public Warehouses: Operated by third-party providers, these facilities offer storage solutions to multiple businesses on a short-term or long-term basis. They are ideal for companies that require flexible storage options without the investment in owning a warehouse.
- Private Warehouses: Owned and operated by a single company, private warehouses are tailored to the specific needs of that business. They provide greater control over inventory and operations but require significant capital investment.
- Bonded Warehouses: These are secure storage facilities where imported goods can be stored without immediate payment of customs duties. They are essential for businesses involved in international trade, allowing for deferred duty payments until goods are sold or distributed.
- Climate-Controlled Warehouses: Designed to store perishable or sensitive goods, these warehouses maintain specific temperature and humidity levels to preserve product quality. They are commonly used for food, pharmaceuticals, and certain electronics.
- Smart Warehouses: Incorporating advanced technologies such as automation, robotics, and real-time data analytics, smart warehouses enhance efficiency, accuracy, and inventory management. They represent the future of warehousing in an increasingly digital supply chain.
How Warehouses Work
The operations within a warehouse are structured to ensure efficient storage and handling of goods:- Receiving: Goods are delivered to the warehouse, where they are inspected for quality and quantity before being accepted into inventory.
- Storage: Products are organized and stored in designated areas, utilizing shelving, pallets, or automated systems to maximize space and accessibility.
- Inventory Management: Continuous monitoring of stock levels is essential to maintain accurate records, forecast demand, and plan replenishments.
- Order Fulfillment: When orders are received, items are picked from storage, packed, and prepared for shipment.
- Shipping: Completed orders are dispatched to their next destination, whether it's a retail location, distribution center, or directly to customers.
- Returns Processing: Returned goods are received, inspected, and either restocked, refurbished, or disposed of, depending on their condition and company policies.
3. Fulfillment Centers vs. Warehouses: A Comparative Overview
While both fulfillment centers and warehouses serve as integral components in the storage and distribution of goods, they differ significantly in function, technology integration, and the value they provide to businesses and consumers.
Core Functions and Operations
- Fulfillment Centers: Primarily designed for the rapid processing and shipping of orders directly to consumers. They handle tasks such as picking, packing, and shipping, often within tight timeframes to meet customer expectations for fast delivery.- Warehouses: Focus on the long-term storage of goods. They are used to store large quantities of inventory, which may be distributed to retailers, wholesalers, or other distribution centers as needed.
Technology Integration
- Fulfillment Centers: Leverage advanced technologies, including automation, robotics, and sophisticated warehouse management systems (WMS), to streamline operations and enhance efficiency. These technologies enable real-time inventory tracking and faster order processing.- Warehouses: May utilize basic inventory management systems, but typically have lower levels of automation compared to fulfillment centers. The focus is more on storage optimization than rapid order processing.
Customer Interaction
- Fulfillment Centers: Interact directly with end customers by fulfilling individual orders, handling returns, and providing customer service support. This direct interaction necessitates a higher level of responsiveness and flexibility.- Warehouses: Generally do not interact directly with end customers. Their primary role is to store products until they are needed for distribution to retail locations or fulfillment centers.
Inventory Turnover
- Fulfillment Centers: Characterized by high inventory turnover, with products moving quickly through the facility to meet customer demand.- Warehouses: Have lower inventory turnover rates, as products may be stored for extended periods before distribution.
Cost Considerations
- Fulfillment Centers: May have higher operational costs due to the need for advanced technology and labor for order processing. However, they can offer cost savings through faster delivery times and improved customer satisfaction.- Warehouses: Typically have lower operational costs, making them cost-effective for businesses needing to store large volumes of inventory over longer periods.
Scalability and Flexibility
- Fulfillment Centers: Offer greater scalability and flexibility, allowing businesses to adjust quickly to changes in demand, such as seasonal spikes or promotional events.- Warehouses: Provide stability for long-term storage needs but may lack the flexibility to adapt rapidly to fluctuating demand.
A Comparison Chart
Here's a comprehensive comparison table highlighting the key differences between fulfillment centers and warehouses:|
Feature |
Fulfillment Center | Warehouse |
|---|---|---|
Primary Function |
Order processing, picking, packing, and shipping directly to customers. | Long-term storage of goods and inventory management. |
Storage Duration |
Short-term; inventory moves quickly to fulfill orders. | Long-term; inventory is stored until needed. |
Order Processing |
High-frequency, small-batch orders with quick turnaround times. | Low-frequency, bulk orders; not typically involved in direct order processing. |
Technology Integration |
Advanced systems with automation, real-time tracking, and warehouse management systems (WMS). | Basic to moderate systems; focus on inventory tracking and storage optimization. |
Customer Interaction |
Direct interaction; ships orders directly to end consumers. | Indirect interaction; supplies products to retailers or fulfillment centers. |
Inventory Turnover |
High turnover; products are constantly moving in and out. | Low turnover; products may remain in storage for extended periods. |
Location Strategy |
Strategically located near major population centers to expedite delivery. | Often situated in areas with lower real estate costs; proximity to transportation hubs for bulk distribution. |
Cost Structure |
Higher operational costs due to advanced technology and labor for order fulfillment. | Lower operational costs focused on storage efficiency. |
Scalability |
Highly scalable to accommodate fluctuating order volumes, especially during peak seasons. | Scalable in terms of storage capacity; less flexible in handling rapid changes in order volume. |
Value-Added Services |
Offers services like kitting, custom packaging, returns processing, and customer support. | Limited value-added services; primarily focused on storage and inventory management. |
4. Choosing the Right Solution for Your Business
Selecting between a fulfillment center and a warehouse is a pivotal decision that hinges on various factors, including your business model, operational needs, and growth aspirations. Understanding the distinct functionalities of each can guide you toward the most efficient logistics strategy.
Assessing Your Business Model and Needs
Fulfillment Centers are ideal if:- Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) Focus: Your business primarily sells directly to consumers and requires rapid order processing and shipping.
- High Order Volume: You handle a large number of small orders daily, necessitating efficient pick, pack, and ship operations.
- Scalability: Your business experiences fluctuating demand and needs a flexible solution that can scale quickly.
- Technology Integration: You require real-time inventory tracking and integration with e-commerce platforms.
Warehouses are suitable if:
- Bulk Storage Needs: You need to store large quantities of inventory for extended periods.
- Business-to-Business (B2B) Operations: Your primary operations involve shipping large orders to retailers or distributors.
- Cost Efficiency: You aim to minimize storage costs and do not require rapid order fulfillment.
- In-House Fulfillment: You have the infrastructure to manage order processing internally.
Hybrid Approaches
Many businesses find value in combining both fulfillment centers and warehouses to optimize their supply chain. For instance:- Seasonal Inventory Management: Use warehouses to store off-season products and fulfillment centers for current inventory.
- Geographical Distribution: Maintain warehouses in strategic locations to supply regional fulfillment centers, reducing shipping times and costs.
- Product Segmentation: Store fast-moving products in fulfillment centers for quick dispatch and slower-moving items in warehouses.
Key Considerations
When deciding between a fulfillment center and a warehouse, consider the following:- Order Fulfillment Speed: If rapid delivery is crucial, fulfillment centers are better equipped to meet this demand.
- Inventory Turnover Rate: High turnover favors fulfillment centers, while low turnover aligns with warehouse storage.
- Customer Expectations: E-commerce customers often expect quick delivery, making fulfillment centers more suitable.
- Operational Control: Warehouses offer greater control over inventory management, which may be preferable for some businesses.
- Cost Implications: Evaluate the cost structures of both options, including storage fees, labor costs, and technology investments.
By thoroughly assessing your business's specific needs and aligning them with the capabilities of fulfillment centers and warehouses, you can develop a logistics strategy that enhances efficiency, reduces costs, and improves customer satisfaction.
5. The 2025 Evolution: Trends Reshaping Both Facilities

- Hyperlocalization & MFCs: The "last mile" remains the costliest. Micro-fulfillment Centers (MFCs), small automated sites in urban areas (vacant stores, parking garages), enable 1-2 hour delivery, reducing congestion and emissions. Major retailers (Target, Walmart, Amazon) lead adoption.
- Sustainability Imperative: Green practices are now competitive necessities. Both facilities focus on:
Energy Efficiency: Solar PV, LED lighting, Energy Management Systems (EMS).
Eco-Packaging: Right-sized, biodegradable materials (driven by consumer demand).
Efficient Logistics: Optimized routes, EV fleets for local delivery, reduced returns via better accuracy.
- AI as the Central Nervous System: AI moves beyond forecasting to real-time optimization: dynamic picking routes, predictive maintenance on robots, intelligent workforce scheduling, and autonomous decision-making within "smart" FCs.
- Rise of the 3PL & Scalability: Third-Party Logistics providers, operating vast FC networks, offer SMEs access to cutting-edge tech (automation, AI WMS) and scalable capacity without massive CapEx. The 3PL market is projected to grow significantly (CAGR ~5.48%).
- Blurring Lines (Store-as-Fulfillment): Retail stores increasingly act as mini-FCs, fulfilling local online orders via curbside pickup or local delivery (e.g., Target's model).
- Cybersecurity Focus: As automation and IoT devices proliferate, protecting operational technology (OT) networks from cyberattacks becomes paramount, especially in highly automated FCs.
2025 Capabilities & Strategic Focus
Trend/Feature |
Warehouse (2025 Focus) | Fulfillment Center (2025 Focus) |
|---|---|---|
Location Strategy |
Cost-optimized (industrial zones) | Proximity-Optimized (Urban MFCs, Regional Hubs) |
Automation Priority |
Efficiency & Safety (e.g., automated cranes) | Speed, Accuracy & Labor Shortage Mitigation (AMRs, AS/RS, AI) |
AI/ML Application |
Basic Inventory Forecasting | Predictive Fulfillment, Real-time Optimization, Robotics Control |
Sustainability Driver |
Energy Management (Lighting/ HVAC) | Right-sized Packaging, EV Fleets, Hyperlocal Efficiency |
Labor Trend |
Retention, Equipment Operation | Upskilling, Cobot Collaboration, Wearable Tech |
Dominant User Model |
Owned/Leased, Large Enterprises | 3PL Partnerships, Scalable Solutions for SMBs |
6. SendFromChina's Warehouse and Fulfillment Center in China
SendFromChina (SFC) is a leading third-party logistics provider based in China, offering comprehensive warehousing and fulfillment services. Their facilities are equipped with advanced technologies to manage inventory efficiently and process orders swiftly.
Key Features:
- Integrated Services: SFC provides end-to-end solutions, including inventory management, order processing, and global shipping.
- Technology-Driven Operations: Utilizing sophisticated software systems, SFC ensures real-time tracking and seamless integration with e-commerce platforms.
- Scalability: Their services are designed to accommodate businesses of various sizes, providing flexibility during peak demand periods.
7. Conclusion
Understanding the differences between fulfillment centers and warehouses is essential for businesses aiming to optimize their supply chain operations. While warehouses focus on long-term storage, fulfillment centers are geared towards rapid order processing and direct-to-consumer delivery. As the logistics landscape continues to evolve in 2025, integrating both facilities strategically can provide a competitive advantage, ensuring efficiency, scalability, and customer satisfaction.8. FAQs
Q1: Can a business use both a warehouse and a fulfillment center?
Yes, many businesses utilize warehouses for bulk storage and fulfillment centers for processing and shipping orders.Q2: Are fulfillment centers only for e-commerce businesses?
While primarily used by e-commerce businesses, fulfillment centers can also serve B2B operations requiring efficient order processing.Q3: How do fulfillment centers handle returns?
Fulfillment centers manage returns by inspecting, restocking, or disposing of returned items based on the business's policies.Q4: Is automation common in modern warehouses?
Yes, many warehouses are adopting automation technologies to improve efficiency and accuracy in inventory management.Q5: What factors should I consider when choosing between a warehouse and a fulfillment center?
Consider your business model, inventory turnover, scalability needs, geographical reach, and cost implications to determine the best fit. Post Views:1295
Post Views:1295
Copyright statement: The copyright of this article belongs to the original author. Please indicate the source for reprinting.
Previous Post
Work in Process Inventory Explained: Meaning, Formula, and Importance
Next Post
Inventory Days on Hand: What It Is, Why It Matters, and How to Calculate It
TAGS
Hot Research
Recent News
Get a Custom China Fulfillment Solution with FREE Storage for 30 Days
 Want to know about our services, fees or receive a custom quote?
Want to know about our services, fees or receive a custom quote?
 Please fill out the form on the right and we will get back to you within a business day.
Please fill out the form on the right and we will get back to you within a business day.
 The more information you provide, the better our initial response
will be.
The more information you provide, the better our initial response
will be.




 TAGS:
TAGS: