Table of Contents
What Are Shipping Barcodes & How 3PLs Use Shipping Barcodes
Time: Sep 09,2024 Author: SFC Source: www.sendfromchina.com
1. What Are Shipping Barcodes
2. Types of Shipping Barcodes
2.1 Shipping Barcode
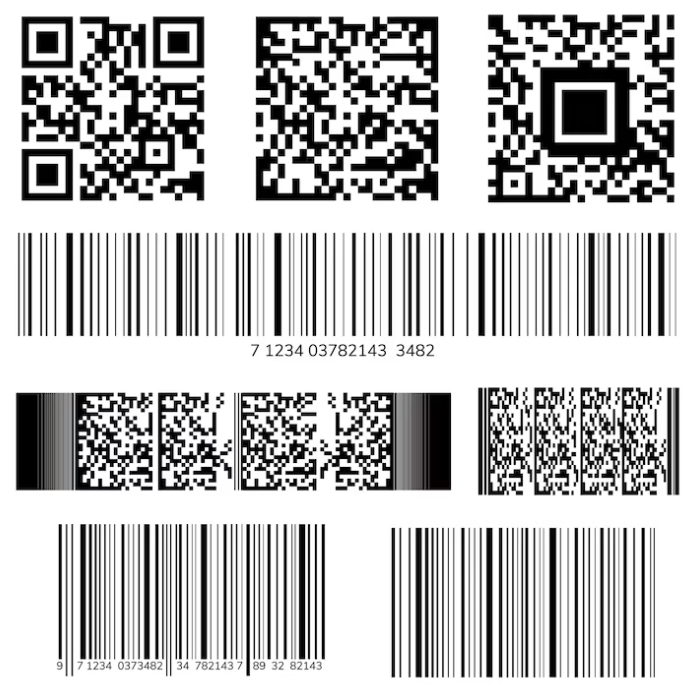
Types of Shipping Barcodes:
Code 128
- Used for tracking numbers on shipping labels.
- Common in logistics due to its ability to encode a wide range of characters in a compact form.
GS1-128 (formerly UCC/EAN-128)
- Provides additional data, such as batch numbers, serial numbers, and expiration dates.
- Widely used in logistics for enhanced tracking and inventory control.
Interleaved 2 of 5 (ITF)
- Numeric-only barcode, often used on carton-level packaging and shipping labels.
- Suitable for fast-paced environments, such as conveyor belts in warehouses.
MaxiCode
- A 2D barcode designed specifically for high-speed scanning in logistics.
- Used by couriers like UPS; can be read even if partially damaged.
PDF417
- A stacked linear barcode that can encode large amounts of text or data.
- Often used for shipping labels, boarding passes, and other logistics documents.
Aztec Code
- A 2D barcode that can be read even if part of it is damaged.
- Increasingly used in shipping labels and transportation tickets.
QR Code
- Used for adding supplementary information to packages, like URLs or handling instructions.
- Not traditionally used for shipping but gaining popularity for customer engagement and mobile scanning.
2.2 Product Barcode
Types of Product Barcodes
UPC (Universal Product Code)
- A 12-digit barcode commonly used in the United States and Canada for retail products.
- Encodes product identification information for point-of-sale systems.
EAN (European Article Number)
- A 13-digit barcode used internationally, particularly in Europe, for product identification.
- Similar in function to UPC, commonly found on consumer goods.
Code 39
- Can encode both letters and numbers.
- Used for inventory management, asset tracking, and sometimes on product packaging.
Data Matrix
- A 2D barcode that can encode large amounts of data in a small space.
- Used for small items, products requiring detailed information like serial numbers, or in sectors like electronics and pharmaceuticals.
QR Cod
- Used on products for marketing purposes, such as linking to websites or providing additional product information.
- Can also be used for inventory management and tracking in some applications.
3. How Do Shipping Barcodes Work

Encoding Information
Data such as product IDs, destination addresses, and tracking numbers are encoded into a barcode format using specific algorithms.Printing Barcodes
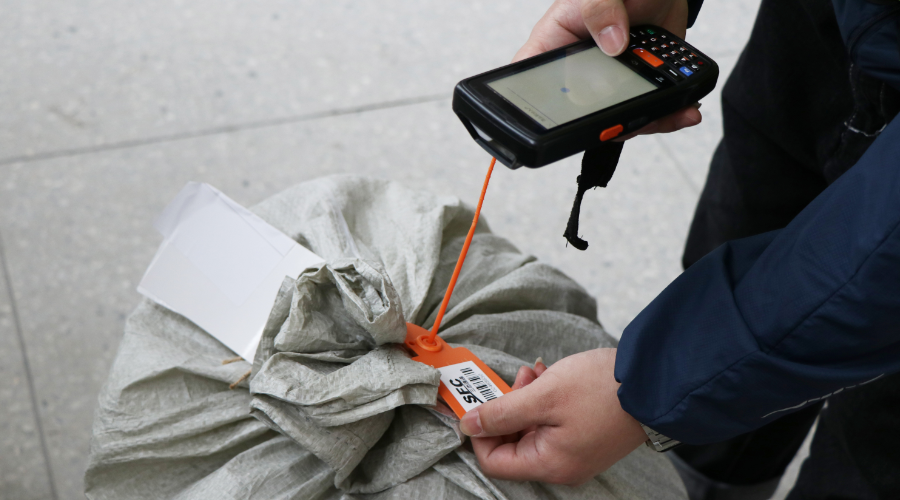
The encoded data is printed onto shipping labels or directly on packaging using thermal printers.Scanning Barcodes
As packages move through the supply chain, barcode scanners read the barcodes at various checkpoints—such as warehouses, sorting facilities, and delivery vehicles.Data Transmission
The scanned data is transmitted to centralized databases, updating the package’s status in real-time and ensuring accurate tracking and delivery.4. How 3PLs Use Shipping Barcodes

Inventory Management
- Track Stock Levels: Barcode scanning provides real-time updates on inventory levels, reducing the risk of overstocking or stockouts.
- Monitor Stock Movements: Every time an item is picked, packed, or shipped, it is scanned, creating a detailed record of stock movements.
Order Tracking and Accuracy
- Reducing Errors: By scanning barcodes during picking and packing, 3PLs can verify that the right products are being shipped, significantly reducing the likelihood of errors.
- Real-Time Updates: Barcodes provide real-time tracking information, allowing 3PLs to offer customers up-to-date status updates on their orders.
Streamlining Returns
- Efficient Returns Processing: Barcodes on return labels allow 3PLs to quickly scan and process returns, updating inventory levels and issuing refunds faster.
- Enhanced Visibility: Barcodes provide clear data on return reasons and product conditions, helping 3PLs manage restocking and reselling processes more efficiently.
5. What Role Does Shipping Barcode Play in Order Fulfillment

Shipping from Manufacturer/Supplier
Arrival at the Warehouse
Picking from Storage
Carrier Pickup
In Transit
Final Delivery
6. Get Started with SFC Services
What Makes SFC Special
Over 17 Years of 3PL and Order Fulfillment ExperienceAll-in-one Tracking Number
Popular Platform API Integration
30 Days of Free Storage
No Hidden Fee
Custom Packaging
Worldwide shipping solutions
Value-added Services
7. FAQs
1. What is the difference between 1D and 2D shipping barcodes?
2. How do shipping barcodes improve inventory management for 3PLs?
3. Can QR codes be used as shipping barcodes?
4. How do barcodes help reduce errors in order fulfillment?
5. What are GS1 barcodes, and why are they important?
 Post Views:6932
Post Views:6932
Copyright statement: The copyright of this article belongs to the original author. Please indicate the source for reprinting.
Previous Post
What to Consider When Finding the Most Profitable Dropshipping Niches
Next Post
What Is a Fulfillment House? Why You Need a Fulfillment House
TAGS
Hot Research
Get a Custom China Fulfillment Solution with FREE Storage for 30 Days
 Want to know about our services, fees or receive a custom quote?
Want to know about our services, fees or receive a custom quote?
 Please fill out the form on the right and we will get back to you within a business day.
Please fill out the form on the right and we will get back to you within a business day.
 The more information you provide, the better our initial response
will be.
The more information you provide, the better our initial response
will be.





 TAGS:
TAGS: